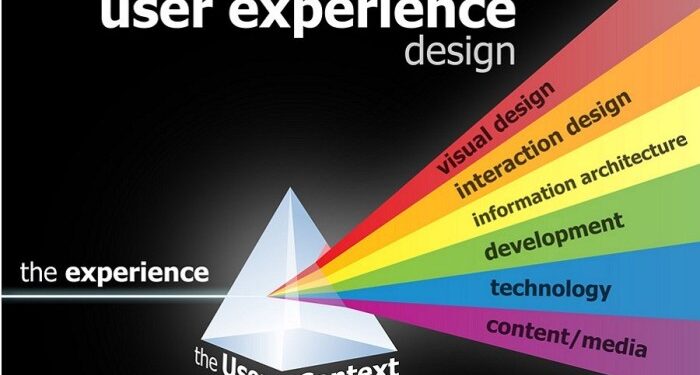
Diving into the realm of user experience design, this introduction sets the stage for an in-depth exploration of the topic. From defining key concepts to discussing practical applications, readers will embark on a journey filled with insights and knowledge.
As we unravel the intricacies of user experience design, we will uncover how it shapes the digital landscape and influences the way users interact with products and services.
What is User Experience Design?
User Experience Design (UX Design) is the process of creating products or services that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users. It involves understanding the needs and behaviors of users, as well as designing solutions that are intuitive, easy to use, and visually appealing.User Experience Design is crucial in product development as it directly impacts how users interact with a product or service.
A well-designed user experience can lead to increased user satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement, ultimately driving business success. On the other hand, a poor user experience can result in frustration, abandonment, and negative reviews.
Key Principles of User Experience Design
- Understand the User: Conduct research to gain insights into user needs, goals, and preferences.
- Usability: Design products that are easy to use and navigate, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in design elements, interactions, and language throughout the product.
- Accessibility: Ensure that the product is accessible to users of all abilities, including those with disabilities.
- Feedback: Incorporate feedback loops to gather user input and continuously improve the user experience.
- Visual Design: Use visual elements such as color, typography, and imagery to enhance the overall user experience.
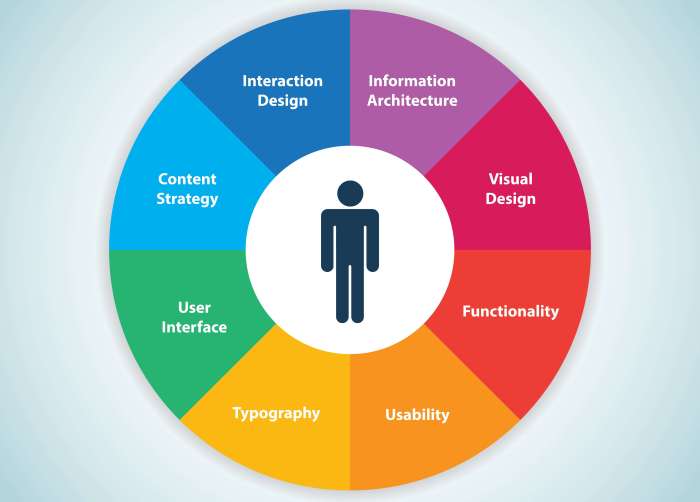
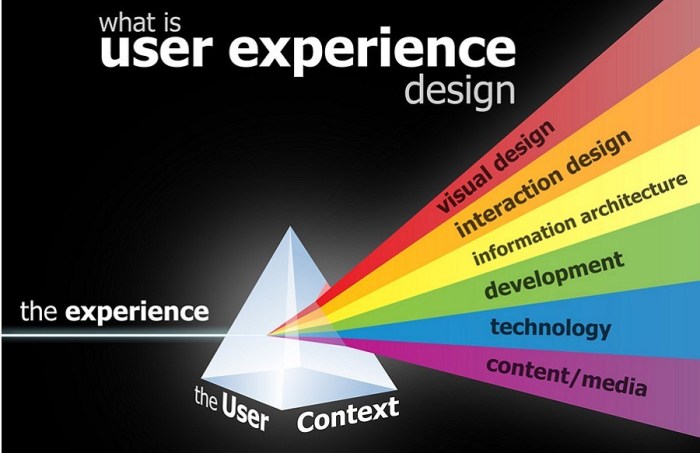
Elements of User Experience Design
User Experience Design encompasses various core elements that work together to create a seamless and enjoyable experience for users interacting with a product or service. Each element plays a crucial role in shaping how users perceive and engage with a digital platform.
1. Information Architecture
Information architecture involves organizing and structuring content in a way that is intuitive and easy for users to navigate. By creating clear paths and categorizing information logically, users can quickly find what they are looking for. For example, a well-designed menu on a website makes it effortless for users to locate different sections and access relevant information, enhancing the overall user experience.
2. Interaction Design
Interaction design focuses on designing interactive elements that allow users to engage with a product. This includes elements such as buttons, forms, and animations that guide users through the interface. For instance, interactive feedback like hover effects or button animations provide users with visual cues and feedback, making interactions more engaging and user-friendly.
3. Visual Design
Visual design involves creating a visually appealing interface that aligns with the brand and enhances usability. This includes aspects like color schemes, typography, and imagery that contribute to the overall look and feel of the product. A visually well-designed interface not only attracts users but also improves readability and usability, ultimately enhancing the user experience.
4. Usability
Usability focuses on ensuring that a product is easy to use and understand. This involves conducting user testing, gathering feedback, and making iterative improvements to enhance the user experience. For example, optimizing the checkout process on an e-commerce website by reducing the number of steps and simplifying form fields can significantly improve usability and overall user satisfaction.
5. Accessibility
Accessibility is about designing products and services that are inclusive and can be used by people of all abilities. This includes considerations such as providing alternative text for images, implementing keyboard navigation, and ensuring compatibility with assistive technologies. By making products accessible, designers can create a more inclusive user experience that caters to a diverse range of users.
User Research in User Experience Design
User research plays a crucial role in user experience design as it helps designers understand the needs, behaviors, and preferences of the target users. By conducting user research, designers can create products and services that are tailored to meet users' expectations, leading to improved overall user satisfaction.
Methods of Conducting User Research
- Surveys: Gathering feedback from a large group of users to identify common patterns and trends.
- Interviews: Conducting one-on-one or group interviews to delve deeper into users' thoughts and experiences.
- Observation: Observing users in their natural environment to understand how they interact with products or services.
- Usability Testing: Testing prototypes with actual users to identify usability issues and gather feedback.
Examples of User Research Influencing Design Decisions
- After conducting user interviews, a design team discovered that users preferred a simpler navigation menu, leading them to redesign the menu for better usability.
- Through usability testing, designers found that users struggled to complete a certain task on a website, prompting them to make adjustments to the layout and interface to improve user flow.
- By analyzing survey data, a product team identified a feature that was highly requested by users, leading them to prioritize its development in the next product update.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is a crucial step in the user experience design process that involves evaluating a product or service by testing it with representative users to identify areas of improvement. This method helps in ensuring that the final product meets the needs and expectations of the users.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Conduct Usability Testing
- Define objectives: Clearly Artikel the goals and objectives of the usability test.
- Recruit participants: Select a diverse group of participants who represent the target audience.
- Create test scenarios: Develop realistic tasks that users will perform during the test.
- Conduct the test: Observe participants as they interact with the product and collect feedback.
- Analyze results: Evaluate the data collected during the test to identify usability issues.
- Iterate and improve: Implement changes based on the feedback received to enhance the user experience.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid During Usability Testing
- Biased facilitation: Avoid leading participants or providing hints that may influence their behavior.
- Ignoring negative feedback: Pay attention to all feedback, especially criticism, as it often highlights areas for improvement.
- Testing with the wrong audience: Ensure that the participants represent the actual user base to get accurate feedback.
- Overloading participants: Keep tasks simple and focused to prevent overwhelming participants.
- Not iterating on feedback: Use the insights gained from usability testing to make tangible improvements to the product.
User Interface Design
User Interface Design is a crucial aspect of the overall User Experience Design process. It focuses on the visual elements of a product or service that users interact with directly. This includes elements such as buttons, menus, icons, and overall layout.
Differentiation from User Experience Design
User Interface Design specifically deals with the look and feel of a product, focusing on enhancing usability and accessibility through visual design. On the other hand, User Experience Design encompasses a broader scope, considering the overall user journey, emotions, and satisfaction throughout the entire interaction with a product or service.
Importance of User Interface Design
User Interface Design plays a critical role in enhancing User Experience by ensuring that the interface is intuitive, visually appealing, and easy to navigate. A well-designed interface can significantly impact user engagement, satisfaction, and ultimately, the success of a product or service.
Examples of Successful User Interface Design Implementations
Apple's iOS interface
Known for its clean and user-friendly design, Apple's iOS interface has set the standard for mobile user interfaces.
Google's Material Design
Google's Material Design principles prioritize user experience by focusing on consistency, accessibility, and visual appeal across different devices and platforms.
Airbnb's intuitive search and booking interface
Airbnb's interface allows users to easily search for accommodations, view photos, read reviews, and book their stay with minimal effort, enhancing the overall user experience.
Accessibility in User Experience Design
Accessibility plays a crucial role in user experience design as it ensures that all users, including those with disabilities, can access and interact with digital products easily and effectively. By designing with accessibility in mind, designers can create inclusive experiences that cater to a diverse range of users.
Importance of Accessibility in User Experience Design
Designing with accessibility in mind not only benefits users with disabilities but also enhances the overall user experience for all users. It helps improve usability, increases audience reach, and ensures compliance with accessibility standards and regulations.
Best Practices for Designing Accessible User Experiences
- Provide alternative text for images to assist users with visual impairments.
- Ensure proper color contrast for readability and usability.
- Use descriptive and meaningful link text for screen readers.
- Implement keyboard navigation for users who cannot use a mouse.
- Test your design with accessibility tools and real users with disabilities.
Examples of How Accessible Design Benefits All Users
Accessible design not only benefits users with disabilities but also enhances the experience for all users. For example, captions in videos not only help users with hearing impairments but also benefit users in noisy environments or those who prefer muted content.
Similarly, clear and concise content benefits users with cognitive impairments as well as users who are in a hurry and looking for quick information.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, user experience design serves as a crucial foundation for creating meaningful and impactful interactions between users and technology. By understanding its principles and implementing best practices, businesses can elevate their offerings and build lasting relationships with their audience.
FAQ Corner
What is User Experience Design?
User experience design focuses on creating products and services that provide meaningful and seamless experiences for users.
Why is User Experience Design important in product development?
User experience design is vital in product development as it ensures that the end product meets the needs and expectations of users, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
What are the key principles that guide user experience design?
The key principles include usability, accessibility, desirability, and value, all aimed at enhancing the overall user experience.
What is usability testing?
Usability testing involves evaluating a product or service by testing it with real users to uncover usability issues and improve the overall user experience.
What is the difference between user experience design and user interface design?
User experience design focuses on the overall experience of the user, while user interface design deals specifically with the visual and interactive elements of a product.